SQL Server database mail is a critical component of good communication.
Good communication is the key to good database administration in the digital era. Database Mail in SQL Server is a great tool that enables seamless email communication from within your SQL Server environment. In this article, we explore Database Mail’s history, benefits, configuration procedures, troubleshooting techniques, and more to help you use it to its maximum capacity.
Table of Contents
Introduction of Database Mail in SQL Server
A key component of success in contemporary database administration is good communication. Enter Database Mail, a potent capability of Microsoft SQL Server that allows for smooth email communication between your database environment and the outside world. Database Mail turns your SQL Server instance into a dynamic information distribution centre that can transmit real-time notifications, scheduled reports, and query results.
Manual alerts and laborious report production are obsolete. Database Mail revolutionizes the way you engage with your data by allowing you to automate email alerts, easily share insights, and keep stakeholders updated without ever leaving your SQL Server Management Studio.
A Historical Overview of DBMail’s Development:
Database Mail was first introduced in SQL Server 2005 as a critical tool for delivering email notifications straight from the database engine. Since then, It has evolved and been improved to offer cutting-edge features, secure connectivity, and interface with current systems.
Explore LCK_M_IS Wait Type In SQL Server
Advantages of Database Mail in SQL Server
The advantages of using database mail are given below:
Real-time Notifications: With Database Mail, you may configure quick alerts for important events like failed tasks, failures, or database problems. Keep yourself informed and act quickly to solve any possible issues.
Scheduled Reports: This tool automates the periodic transmission of regular reports to specified recipients without requiring direct involvement. It guarantees that stakeholders receive timely information.
Delivery of Query Results: Database Mail lets you email the results of a query to recipients’ email addresses. Sharing data insights or specific information with appropriate stakeholders might be especially helpful.
Integration with apps: Easily integrate email communication into your apps to improve user experience and promote timely system communication.
Centralised Configuration: Use SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) as a simple and reliable setting up and upkeep platform for email settings and setups.
Flexibility and Customization: To ensure the right information is conveyed to the right individuals, customise the email’s content, layout, and recipients to meet your specific needs.
Audit Trail: Database Mail, which records every email sent in the system tables, makes keeping an audit trail for compliance and oversight purposes possible.
Disadvantages of Database Mail in SQL Server
SMTP Server Dependency: Email delivery with Database Mail depends on an external Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server. Any SMTP server issues might influence how SQL Server sends emails.
Initial Configuration Difficulty: SMTP servers, profiles, and login credentials may need to be configured while setting up Database Mail. The first setting procedure might be difficult, particularly for those who are unfamiliar with the functionality.
Resource Consumption: Sending many emails, especially those with attachments or massive query results, may use up server resources and hurt performance.
Potential Security Concerns: Database Mail enables encryption, but transmitting sensitive information over email raises security issues, including data leaking or unauthorized access.
Limited Attachment Size: SMTP server limits may limit the size of attachments that may be sent with Database Mail.
Challenges with authentication: Coordinating with network or IT administrators may be necessary when configuring authentication and security settings, such as the SMTP username and password.
Maintenance and Monitoring: Regular maintenance and monitoring are necessary to ensure that emails are delivered and received as intended. This involves handling unsuccessful email transmissions and preserving the SMTP server’s functionality.
Permission Required to Configure Database Mail
To start the configuration of Database Mail, we should have administrator access on the server.
To manage Database mails, we should be a member of the “DatabaseMailUserRole” role in the msdb database.
Use msdb;
go
EXEC sp_addrolemember 'DatabaseMailUserRole','Test';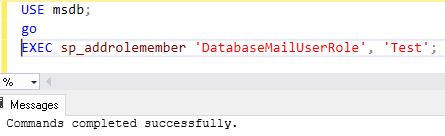
You may also like “The Understanding SQL Server Allocation Checks with DBCC CHECKALLOC” article.
Pre-requisites to configure Database Mail
Microsoft SQL Server often needs administrator rights and specific permissions to configure Database Mail properly. The procedures and permissions required for configuring Database Mail are summarised below:
- SQL Server Authentication: We need administrator access to the server to begin configuring Database Mail.
- Database Mail Role: To manage Database emails, we should be members of the “DatabaseMailUserRole” role in the msdb database.
- DatabaseMailUserRole Membership: To join the “DatabaseMailUserRole,” if you aren’t already, run the T-SQL query below:
USE MSDB;
go
EXEC sp_addrolemember 'DatabaseMailUserRole', '<UserName>';
go- SMTP Configuration: You must have the SMTP server information, including the server name, port, authentication information, and a legitimate sender email address.
- Permissions for the SMTP Server: Verify that the SQL Server instance has the necessary network access and permissions to send emails via the SMTP server. The SMTP server and SQL Server may need to have their firewalls or security settings set up to accomplish this.
- SQL Server Agent: To use Database Mail, the SQL Server Agent service must be operating because it queues and delivers emails. Make sure the SQL Server Agent is operational and configured correctly.
- Database Mail Profile: Create a Database Mail profile to save the email configuration settings. You require the “DatabaseMailUserRole” role to create and manage profiles.
- Profile setup: Set the SMTP server information, authentication preferences, and other necessary setup choices for the Database Mail profile.
You may also like this article: DBCC SHRINKFILE: A Comprehensive Guide to Database Maintenance
Step-By-Step Guide To Configuring SQL Server Database Mail
Step 1: In the first step. Just connect to the SQL Instance using SSMS.
Connect to the SQL instance where database mail configuration is done using the administrator credentials.
Step 2: Turn on Database Mail:
Expand Object Explorer & Right-click on the “Management” node and select “Database Mail Configuration Manager”.
It’ll display the Database Mail Configuration Wizard.

Step 3: Configure Profile & account for database mail:
Select “Next”.
After selecting “Set up Database Mail ……. tasks, ” click the “Next” button.
Specify the profile name and description and press “Add…”.
Now, enter the SMTP server details like name, port, encryption options, etc.
Also, specify basic authentication with username and password.
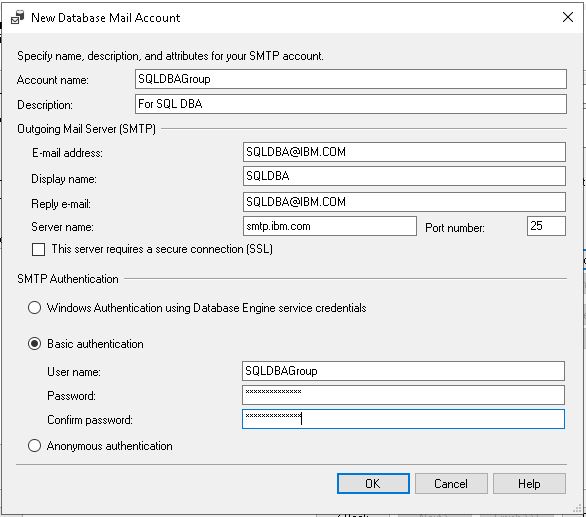
Step 4: Manage the Security
If needed, grant the “DatabaseMailUserRole” role to a specific user(s). This role is needed to send emails.
Then click on the “Next” button.
Step 5: Complete Wizard:
Finally, validate the configuration settings and press the “Finish” button to save them in the system.
Step 6: Now, Configure the SQL Server Agent:
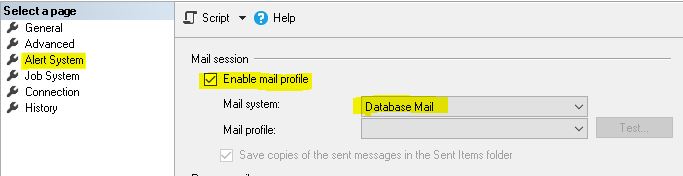
Open SSMS, Expand the SQL Instance, Right-Click on the SQL Server Agent, and select “Properties.”
Now, go to the “Alert System” section and select “Enable mail profile”.
Select the profile & Press the “OK” button.
Step 7: Test Database Mail
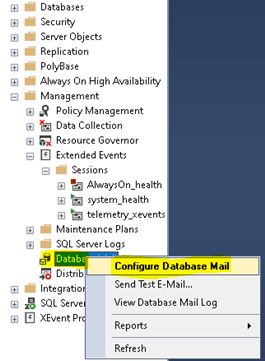
Now, the setup is ready for testing. Open SSMS, Expand the SQL instance, go to “Management,” and select “Database Mail.”
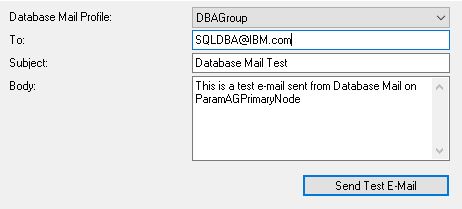
Select “Send Test E-Mail…” after right-clicking on “Database Mail”.
Enter the email address to which we want to receive the test mail.
Lastly, click on the “Send Test Email”.
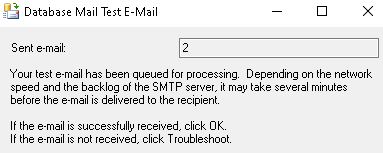
Step 8: Monitor and Troubleshoot
Closely monitor SQL Server logs and Database Mail-related errors.
In case of any issue, just refer to the logs files to troubleshoot the issue.
Examples
To set Profile for Database Mail in SQL Server
-- To Enable Database Mail in SQL Server
EXEC msdb.dbo.sysmail_configure_sp @enable_mail = '1';
-- To Create a new profile for Database Mail in SQL Server:
EXEC msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_profile_sp
@profile_name = 'SQLDBA',
@description = 'Profile For SQL DBA';
-- To Create a new account for Database Mail in SQL Server
EXEC msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_account_sp
@account_name = 'SQLDBAAccount',
@email_address = '<Email ID of sender>',
@mailserver_name = '<SMTP Server Name>', --smtp.Dish.com
@port = 25,
@enable_ssl = 0, --0 means the SSL is not enabled, 1 means the SSL is enabled.
@username = '<User Name>',
@password = '<Password>';
-- To add the SQL DBA Account with the SQL DBA Profile
EXEC msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_profileaccount_sp
@profile_name = 'SQLDBA',
@account_name = 'SQLDBAAccount',
@sequence_number = 1;How to Send an Email using SQL Server Database Mail
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@profile_name = 'SQLDBA',
@recipients = '<Recipient Email IDs separated by ;>', --'Sagarg@microsoft.com;TripathyA@microsoft.com;'
@subject = 'How to Send a Email using SQL Server Database Mail',
@body = 'How to Send a Email using SQL Server Database Mail'; --Body part of the mail.How to Send an Email with Attachment
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@profile_name = 'SQLDBA',
@recipients = '<Recipient Email IDs separated by ;>', --'Sagarg@microsoft.com;TripA@microsoft.com;'
@subject = 'How to Send a Email with Attachment',
@body = 'How to Send a Email with Attachment', --Body part of the mail.
@file_attachments = ''; --Like D:\ReportPath\Report_20042024_1530.txtHow to attach the query result with email & Send to the SQL Server
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@profile_name = 'SQLDBA',
@recipients = '<Recipient Email IDs separated by ;>', --'Sagg@microsoft.com;TripA@microsoft.com;',
@subject = 'How to attach the query result with email & Send in SQL Server',
@query = 'SELECT * FROM DBADB.dbo.Inventory WHERE IsActive=1',
@attach_query_result_as_file = 1, -- We need to set the value as 1 for this parameter if we want to attach the query result
@query_attachment_filename = 'AttachQueryResult.csv';How to Send Email After Completion of SQL Server Agent Job
USE msdb;
EXEC dbo.sp_update_job
@job_name = 'SQL DBA - Maintenance Job - Database Full Backup - Weekly',
@notify_level_eventlog = 0,
@notify_level_email = 2,
@notify_email_operator_name = 'The SQL Agent Job : SQL DBA - Maintenance Job - Database Full Backup - Weekly has been completed successfully on ParamPrimaryNode01.';How to Send Mail with HTML formatted report
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@profile_name = 'SQLDBA',
@recipients = <Recipient Email IDs separated by ;>'', --'Sagg@microsoft.com;TripA@microsoft.com;'
@subject = 'How to Send mail with HTML formatted report',
@body = 'This is the test mail with HTML tags & data. Database mail is the key part of SQL Server.',
@body_format = 'HTML'; --If our body part has HTML codes, we need to specify HTML for this parameter.How to set the priority of the mail
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@profile_name = 'SQLDBA',
@recipients = '<Recipient Email IDs separated by ;>', --'Sagg@microsoft.com;TripA@microsoft.com;',
@subject = 'High Priority Email',
@body = 'Urgent Email.',
@importance = 'High', -- to Set the priority of the mail, we need to specify the priority value here.
@sensitivity = 'Private'; -- to Set the sensitivity of the mail, we need to specify the sensitivity value here.How to send the mail with Carbon Copy (CC) & Blind Carbon Copy (BCC)
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@profile_name = 'SQLDBA',
@recipients = '<Recipient Email IDs separated by ;>', --'Sagg@microsoft.com;TripA@microsoft.com;'
@copy_recipients = '<CC Recipient Email IDs separated by ;>',
@blind_copy_recipients = '<BCC Recipient Email IDs separated by ;>',
@subject = 'How to send the mail with Carbon Copy (CC) & Blind Carbon Copy (BCC)',
@body = 'The latest version of Microsoft RDMBS is know as Microsoft SQL Server 2022.';How to Customize Header Value & Send Email
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@profile_name = 'SQLDBA',
@recipients = '<Recipient Email IDs separated by ;>', --'Sagg@microsoft.com;TripA@microsoft.com;'
@subject = 'How to Customize Header value & Send Email',
@body = 'The latest version of Microsoft RDMBS is know as Microsoft SQL Server 2022.',
@body_format = 'TEXT',
@additional_headers = 'Reply-To: ReplyToEmailID@microsoft.com';These examples show off some of the other features that SQL Server Database Mail can do, like sending emails with HTML formatting, indicating the significance and sensitivity of the message, sending emails with CC and BCC to many recipients, and adding custom headers. Personalize the samples to fit your own needs and tastes.
Conclusion
Database Mail in SQL Server provides real-time notifications, scheduled reports, and seamless integration to fill the gap between your database and effective communication. By understanding its setup, configuration, and troubleshooting, you can empower your SQL Server environment to communicate effectively, keeping you informed and in charge.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can I use Gmail as my SMTP server for Database Mail?
Ans: Yes, by configuring Gmail’s SMTP settings in SQL Server.
Q: Can I use Database Mail with Azure SQL Database?
Ans: No, Database Mail is not supported in Azure SQL Database.
Q: Can I send attachments using Database Mail?
Ans: Yes, Database Mail supports sending attachments.
Q: What is Database Mail for SQL Server?
Ans: The database engine can send emails straight from within SQL Server thanks to a function called SQL Server Database Mail. This enables users to send email notifications, alerts, and reports and customize email settings, including SMTP server information.
Q: How may SQL Server Database Mail be configured and enabled?
Ans: To enable and customize the Database Mail feature in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), you must set up the SMTP server information and create Database Mail profiles and accounts. Comprehensive instructions are available in the SQL Server documentation.
Q: What advantages does SQL Server Database Mail offer?
Ans: There are various advantages to using SQL Server Database Mail, such as:
Email alerts, reports, and notifications are easily sent thanks to a smooth interaction with SQL Server.
Central administration of SQL Server’s email configurations and settings.
Support for asynchronous email sending that doesn’t interfere with database functions.
Options for flexible configuration that allow you to name email recipients, subject lines, and body information.
Q: Is it possible to send notifications of database errors using SQL Server Database Mail?
Ans: Yes, Database Mail is frequently used to send alerts for significant problems, job failures, and database maintenance activities, among other database error messages. Database Mail can be set up to send emails in response to particular error circumstances or events.
Q: Is Database Mail for SQL Server Secure?
Ans: SQL Server Database Mail supports Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption to enable secure connections with SMTP servers. Additionally, it offers choices for limiting access to Database Mail profiles and accounts and defining login credentials. However, it’s crucial to adhere to security best practices, which include encrypting private emails and monitoring email traffic for security risks.
Q: Is it possible to transmit attachments using SQL Server Database Mail?
Ans: Database Mail’s attachment-sending functionality allows us to attach files, reports, or query results to emails. It can also be set up to accept attachments from external disk files or straight from SQL Server queries.
Q: How can SQL Server Database Mail problems be resolved?
Ans: Configuration failures, network connectivity issues, or SMTP server issues are common problems with Database Mail. Issues with Database Mail can be resolved by examining the Database Mail log in SSMS, confirming the settings for the SMTP server, and utilizing the “Send Test Email” option in SSMS to test email delivery. Furthermore, examining error messages and referring to SQL Server documentation can aid in accurately diagnosing and resolving problems.
Review the below articles also
1. Understanding Indexes in SQL Server: A Complete & Comprehensive Guide
2. Unlocking Performance and Efficiency with ColumnStore Indexes
Dbcc Freeproccache: A powerful command
Extended Events in SQL Server: A Deep Dive


Right now it sounds like WordPress is the preferred blogging platform out there right now.
I highly recommend this website.
Excellent goods from you, man. I’ve understand your stuff previous to and you’re just extremely wonderful.
I really like what you’ve acquired here, certainly like what you are stating and the way in which you say it.
You make it entertaining and you still care for to keep it sensible.
I can’t wait to read much more from you.
This is really a great website.
I liked your website.
You hit the nail on the top and defined the whole thing without side effects; people could take a signal.
I will likely be back to your website to get more.
Thanks
Hello there,
I found your site by means of Google at the same time as searching for a comparable topic. Your website got here up, it seems to be good.
I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Hello there, just changed into aware of your blog through Google,
and located that it’s truly informative.
I will be grateful in the event you proceed this in future.
A lot of other folks might be benefited from your writing.
Cheers!