In MS SQL Server, multiple SQL Server Reports are already available for developers and administrators to provide an essential mechanism to keep a close eye on the performance of the SQL instance, databases, troubleshoot issues, and analyze data efficiently. These reports are pre-defined, and we can customize it. It can be extended according to the organization’s needs. In this article, we examine the history of these reports, types of reports, the required permissions to use these reports, advantages and disadvantages of these reports, best practices, A few common issues related to these reports, and very important-A few interview questions with Solution.
Table of Contents
📖 Introduction to SQL Server Reports
In Microsoft SQL Server, multiple predefined or custom-generated reports are available for developers as well we administrators that deliver structured insights about databases, server performance, configuration, and security. Reports help database administrators identify system bottlenecks, monitor resources, analyze growth trends, and maintain compliance. It plays an important role in proactive health check, database management and effective decision-making.
🏛 A Glimpse into History
These reports were first introduced with Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio in SQL Server 2005. Over time, Microsoft enhanced reporting capabilities, integrating SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) and expanding the variety of out-of-the-box reports. Today, SQL Server Reports in SQL Server are tightly linked with both SSMS and SSRS, offering administrators deeper visibility and actionable insights.
✅ Advantages of SQL Server Reports
A few advantages of SQL Server Reports are given below for more clarity & better understanding:
✅ Seamless Integration with SQL Server
- SQL Server Reports work natively with SQL Server databases, Analysis Services (SSAS), and Integration Services (SSIS).
- You can generate reports directly from structured or multidimensional data sources without additional tools.
✅ Variety of Report Formats
- Supports tabular, matrix, chart, KPI, gauge, and free-form reports.
- Reports can be interactive (drill-down, drill-through) or static (summary, detail).
✅ Easy to Export the report
- We can export these reports easily in multiple formats like PDF, Excel, Word, CSV, XML, and HTML.
- We can also easily share these reports with stakeholders in their preferred format.
✅ Web-Based Access – Any Time
- Such reports can be accessed any time & Any where via a web browser.
- It supports mobile reporting through Power BI Report Server or SSRS mobile reports.
✅ Cost-Effective
- Included with SQL Server (Standard and Enterprise editions).
- No need for additional third-party reporting tools in most cases.
✅ Scalability and Performance
- Supports large datasets and optimised report rendering.
- Can handle both small departmental reporting and enterprise-wide reporting needs.
🔹 Different types of predefined reports
SQL Server provides a large set of SSRS reports for developers as well as administrators, such as:
🔹 Standard Reports in SSMS:-
i. Disk Usage Report – It helps track data file size, log file size, reserved space, and unallocated space to avoid storage-related issues.
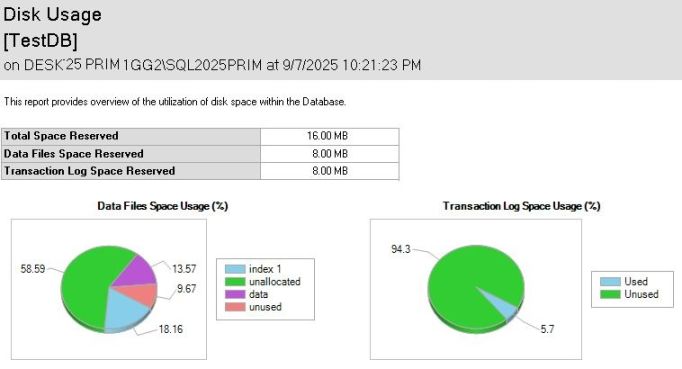
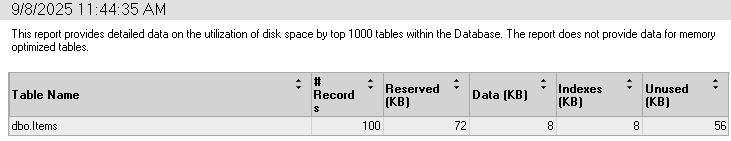
ii. Disk Usage by Top Tables Report – Useful for identifying large tables that may need archiving, partitioning, or indexing optimisation.
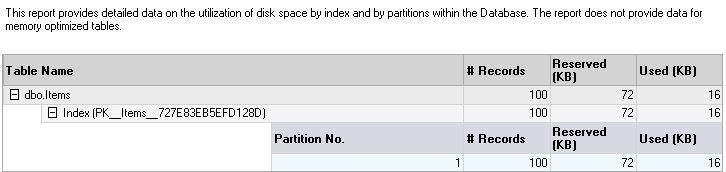
iii. Disk Usage by Partition Report – Important for partitioned tables where storage distribution across partitions matters for query performance and maintenance.
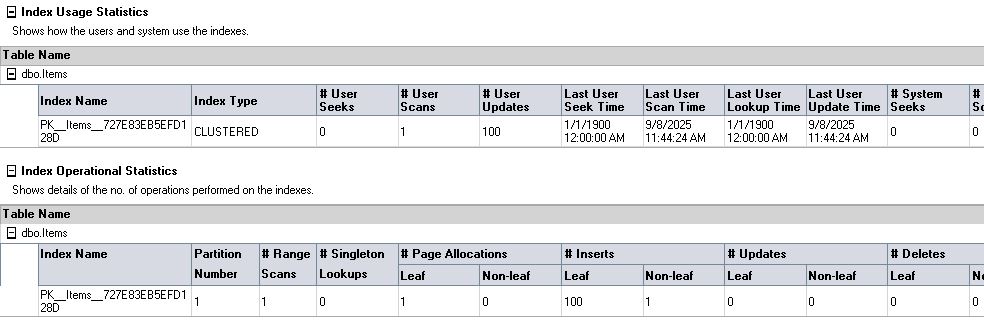
iv. Index Usage Statistics Report – Helps DBAs determine unused indexes (candidates for removal) and heavily used indexes (candidates for optimisation).
v. Schema Changes History Report – Useful for auditing, troubleshooting unexpected behaviour, or verifying deployment changes.
vi. Top Transactions by Age Report – Helps identify open/long transactions that may cause blocking, high log usage, or performance bottlenecks.
vii. Backup and Restore Events Report – Useful for audit compliance and verifying that backups/restores are running as expected.
viii. Transaction Log Shipping Status Report – Helps ensure disaster recovery (DR) configurations are healthy and log shipping is working properly.
ix. All blocking transactions Report – Essential for troubleshooting performance issues caused by locking and concurrency problems.
x. All transaction Report – Useful for real-time monitoring of database activity and troubleshooting transaction-related issues.
🔹 SQL Server Agent related reports
i. Job Activity Reports
- It helps to monitor which jobs are currently running or waiting.
- It helps to quickly identify failed or long-running jobs.
- Helpful during production monitoring when DBAs need a live snapshot of job activity.
ii. Job History Reports
- It helps to troubleshoot failed jobs by reviewing detailed error messages.
- It helps to analyse job run frequency and duration trends over time.
- Useful for capacity planning and identifying performance bottlenecks in scheduled jobs.
🔹 Custom Reports
i. User-defined reports created using .rdl files in SSMS.
🔐 Required Permissions to Use SQL Server Reports
For SSMS Standard Reports:
- Membership in the db_datareader role (database-level) or equivalent.
- View Server State permission for server-level reports.
For SSRS Reports:
- Membership in predefined roles such as Browser, Content Manager, Publisher, or custom roles.
- Proper privileges assigned within Report Manager or via SQL Server Management Studio Security settings.
❓ Why SQL Server Reports are Needed
- To keep close eye on the health of the SQL instance as well as the individual database
- To monitor the performance of SQL Server.
- To monitor efficient resource utilization.
- To help DBAs to troubleshoot issues quickly.
- To provide auditing and compliance reports.
- To analyze DB growth trends and plan for scaling.
- To standardize reporting across teams.
🔹 A few Best Practices for SQL Server Reports
A few best practices are given below for more clarity & better understanding:
- Always use built-in SSMS reports for quick result & better understanding & monitor health of SQL Server instance.
- Regularly review and clean unused or outdated reports.
- Keep close eye on role-based security to limit report access.
- Store historical reports separately to track long-term trends.
🏁 Conclusion
Such Reports in Microsoft SQL Server play an important role to keep close eye on the SQL instances or databases, monitoring the performance closely, troubleshooting the problems, and Keep the environment error free & healthy. We can use standard SSMS reports for quick checks and SSRS for advanced reporting, organizations can ensure visibility into their data and infrastructure. By addressing general issues, and taking advantage of the right permissions, these SQL server reports become an indispensable tool for each Database Administrators and developers.
🔹 FAQs: Top 25 Interview Questions
Qns: What are SQL Server Reports in SQL Server?
Ans: Reports that provide insights into databases, performance, and server health.
Qns: Where are standard reports accessed in SSMS?
Ans: Right-click an instance, database, or job, then select Reports → Standard Reports.
Qns: Name three common SSMS reports.
Ans: Disk Usage, Schema Changes History, Index Usage Statistics.
Qns: What is SSRS?
Ans: SQL Server Reporting Services is a platform for designing and deploying advanced reports.
Qns: What are paginated reports in SSRS?
Ans: Reports formatted for printing or detailed document-style output.
Qns: What permissions are needed for viewing server-level reports?
Ans: The VIEW SERVER STATE permission.
Qns: What is the difference between SSMS standard reports and SSRS reports?
Ans: SSMS reports are built-in and predefined; SSRS reports are customizable and interactive.
Qns: What is a drill-through report in SSRS?
Ans: A report that links to another detailed report for deeper insights.
Qns: How do you create a custom SSMS report?
Ans: Develop an .rdl file in Report Designer and load it into SSMS.
Qns: Can SSRS connect to non-SQL Server data sources?
Ans: Yes, via ODBC, OLEDB, and other supported providers.
Qns: What are the linked reports?
Ans: Linked reports are the reports which reuse an existing report definition with different parameters.
Qns: What is a snapshot report?
Ans: A report that captures data at a specific time for historical viewing.
Qns: What causes slow report rendering?
Ans: Poorly optimized queries or insufficient server resources.
Qns: How to troubleshoot missing report data?
Ans: Check dataset queries, filters, and data source connections.
Qns: What is the role of Report Manager in SSRS?
Ans: It manages, secures, and schedules report execution.
Qns: Which SQL Server edition includes SSRS?
Ans: Standard, Enterprise, and Developer editions.
Qns: Can SQL Server Express edition support SSRS?
Ans: Yes, with SSRS Express, but with limitations.
Qns: What tool is used to design SSRS reports?
Ans: Report Builder or SQL Server Data Tools (SSDT).
Qns: Explain the difference between a parameterized report and a snapshot report?
Ans: Parameterized reports accept user inputs; snapshot reports show fixed data.
Qns: How to secure SSRS reports?
Ans: By assigning roles such as Browser, Publisher, or Content Manager.
Qns: What is the default report format in SSRS?
Ans: .rdl (Report Definition Language).
Qns: What is drilldown in SSRS?
Ans: An interactive feature to expand/collapse detailed sections.
Qns: What are subscriptions in SSRS?
Ans: Scheduled deliveries of reports via email or file share.
Qns: What are execution logs in SSRS?
Ans: Logs that store details about report execution, performance, and errors.
Qns: Why are SQL Server Reports important for DBAs?
Ans: They help monitor performance, manage resources, and troubleshoot efficiently.
Review the articles below, also.
LIKE Operator in SQL: Top 5 Best Usage
SQL IN Operator: Top 5 Benefits
Explore Always Encrypted: Top 5 Usage
Explore SQL Server 2025: 5 Best Usage
Explore Top 10 Features of SSMS 21
PostgreSQL vs MySQL: Top 9 Differences
Explore Sequences and Series: Top 5 Usage
SQL Window Functions: Top 5 Best Usage
Explore SQL Commands: Top 25 Commands

