TDE In SQL provides data protection for an organization & it is a major responsibility of database administrators. To safeguard the data of any company, MS SQL Server offers multiple security techniques to secure sensitive data. In this article, we aim to explain everything about TDE in SQL Server, covering its history, implementation, steps, and interview questions.
Table of Contents
🔍 Introduction of TDE in SQL Server
TDE in MS SQL Server is a feature that helps us encrypt the data. Using this technique, we can protect our database files, such as .mdf, .ndf, and .ldf, and also back up files. Unlike column-level encryption, TDE encrypts the entire database transparently, requiring no changes in the application code. The data encryption and decryption in Transparent Data Encryption are managed at the I/O level, ensuring data security without impacting performance overhead.
🏛 A Glimpse into History
The TDE was first introduced in SQL Server 2008 by Microsoft with the Enterprise Edition. Its primary purpose was to help organizations meet compliance requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Initially, TDE was limited to enterprise customers, but later it was included in more editions (such as SQL Server 2019 Standard edition) to broaden accessibility.
✅ Advantages of TDE in SQL Server
A few advantages of using TDE in SQL Server are given below for better understanding:-
✅ Data-at-Rest Protection
To safeguard database files, backup files, and transaction logs of one or more databases.
✅ Regulatory Compliance
It meets international security standards like PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR.
✅ Ease of Implementation
TDE in SQL is easy to implement and manage—no need to change the application code.
✅ Backup Security
TDE in SQL encrypts database backup files also. Hence, encrypted backup files prevent unauthorized restoration on any other environment.
✅ Minimal Performance Impact
It typically creates less than 5–10% overhead on the server.
❌ Disadvantages of TDE in SQL Server
A few disadvantages of using TDE in SQL Server are given below for better understanding:-
❌ No Protection for Data in Transit
TDE in SQL does not encrypt the data during network communications between two end-user servers.
❌ Edition Limitations (older versions)
The previous version of SQL Server restricted the TDE feature to the Enterprise Edition only.
❌ CPU Overhead
It can slightly impact the server’s performance if the environment is resource-intensive.
❌ Complexity in Key Management
If encryption certificates or keys are lost, data will be unrecoverable.
🔐 Required Permissions to Configure TDE in SQL
To configure TDE in SQL Server, the following permissions are required:
- CONTROL permission on the database.
- ALTER ANY CERTIFICATE and VIEW DEFINITION on the certificate.
- CONTROL SERVER or membership in the sysadmin role.
❓ Why TDE in SQL Server is Needed
- It prevents the exposure of sensitive information when storage media is lost or stolen.
- It is essential for organizations subject to data protection regulations.
- Ensures backups and detached database files remain secure.
- Adds a crucial layer of defense to an in-depth strategy.
📌 Best Practices for TDE in SQL Server
- Always back up the Database Encryption Key (DEK) and certificates.
- Store certificates in a secure location, preferably outside the SQL Server host.
- Use strong algorithms like AES_256.
- Monitor performance after enabling TDE in SQL.
- Regularly test backup restore operations with encryption.
- Use Always Encrypted or TLS along with TDE in SQL for comprehensive protection.
🌟 Steps to Implement TDE in SQL Server
Steps to implement TDE in SQL Server in Standalone Environment are given below:
Step 1:- Create a Master Key
First of all, we need to create a Master Key in the master database of source server.
use master;
go;
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'PutStrongPassword@Here';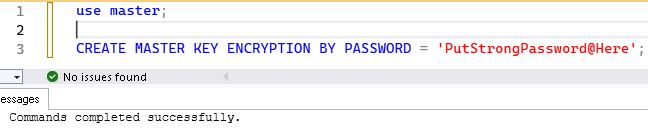
Step 2:- Create a Certificate
Create a Certificate in the master database.
CREATE CERTIFICATE [TDECert_StandAlone] WITH SUBJECT = 'TDE Certificate In StandAlone Environment';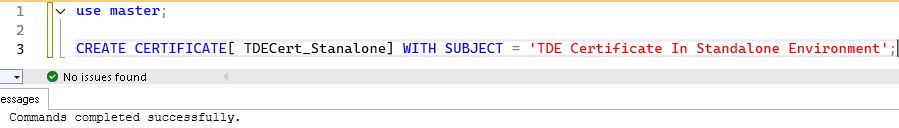
Step 3:- Create a DEK
Create a Database Encryption Key (DEK) in the user database.
USE SQLMonitor;
go
CREATE DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEY
WITH ALGORITHM = AES_256
ENCRYPTION BY SERVER CERTIFICATE TDECert_StandAlone;Step 4:- Create a backup of certificate
Create a backup of certificate for safer side:
use master;
go
BACKUP CERTIFICATE [TDECert_StandAlone]
TO FILE='E:\TDEBackups\Certs\TDECert_StandAlone.certbak'
WITH PRIVATE KEY (file='E:\TDEBackups\Certs\TDECert_StandAlone_PVK.pvkbak',
ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD='PutStrongPassword@Here')
GONote:- In case of below error:
Msg 15151, Level 16, State 1, Line 15 Cannot find the certificate ‘TDECert_StandAlone‘, because it does not exist or you do not have permission.
Verify that the certificate actually exists in the system or not:
USE master;
GO
SELECT name AS CertName, subject AS CertSubject, pvt_key_encryption_type_desc
FROM sys.certificates
WHERE pvt_key_encryption_type='MK';
Try to grand permission on the login id which you are using:
USE master;
GO
GRANT CONTROL ON CERTIFICATE::TDECert_StandAlone TO [DESKTOP-FBG892BF21\sumit];
GOStep 5:- Enable encryption
Enable encryption on the SQLMonitor database.
use master;
go
ALTER DATABASE [SQLMonitor] SET ENCRYPTION ON;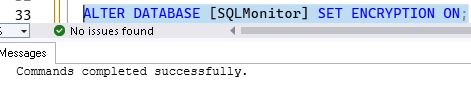
Step 6:- Validate the implementation
Finally, Validate the implementation
USE master;
GO
SELECT DB_Name(dek.database_id) AS [UserDatabaseName],
dek.encryption_state AS [CurrentEncryptionState],
cert.name AS [CertificateName],
cert.thumbprint AS [CertThumbprint]
FROM sys.dm_database_encryption_keys AS dek
JOIN sys.certificates AS cert
ON dek.encryptor_thumbprint = cert.thumbprint;
GO🌟 Steps to Implement TDE in SQL in Always-On Environment
Step 1:- Follow above steps
Follow above steps starting from 1 to 5.
Step 2:- Restore the certificate
Now, restore the certificate on all secondary replicas using the same password.
use master;
go
CREATE CERTIFICATE [TDECert_AGEnvironment]
FROM FILE = 'E:\TDEBackups\Certs\TDECert_AGEnvironment.cer'
WITH PRIVATE KEY (FILE = 'E:\TDEBackups\Certs\TDECert_AGEnvironment_PrivateKey.pvk',
DECRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'PutStrongPassword@Here');
Step 3:- Add the database
Now, Add the required database to the Availability Group.
Step 4:- Verify the encryption
Finally, verify the encryption status on all replicas.
🌟 Steps to Restore a TDE-Encrypted Database on Another Server
Step 1: Execute below query to check the TDE certificate on Source Server
USE master;
GO
SELECT
@@ServerName AS [Server Name],
db.name AS [User Database Name],
dm.encryption_state AS [Current Encryption State],
dm.key_algorithm AS [AlgorithmName],
dm.key_length AS [Key Length],
c.name AS [CertificateName],
c.thumbprint [Certificate Thumbprint]
FROM sys.dm_database_encryption_keys AS dm
JOIN sys.certificates AS c
ON dm.encryptor_thumbprint = c.thumbprint
WHERE dm.database_id = DB_ID('SQLMonitor');
GOStep 2: Now, take the backup the certificate and Private Key from source server
USE master;
GO
BACKUP CERTIFICATE TDECert_StandAlone
TO FILE = 'E:\TDE_Cert\Backup\TDECert_StandAlone.cer'
WITH PRIVATE KEY (
FILE = 'E:\TDE_Cert\Backup\TDECert_StandAlone_PrivateKey.pvk',
ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'PutStrongPassword@Here'
);
GOStep 3: Now, we need to copy Certificate and Private Key files from source server to Destination Server
- TDECert_StandAlone.cer
- TDECert_StandAlone_PrivateKey.pvk
Store them in a secure folder on Destination Server such as: E:\TDE_Certs\
Step 4: Now we need to create a Database Master Key on Destination Server
Before importing the certificate on Destination Server, ensure a Database Master Key (DMK) exists in the master database. If not available, use below script to create new one:
USE master;
GO
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'PutVeryStrongPassword@Here';
GOStep 5: Now, we need to restore the Certificate on Destination Server
USE master;
GO
CREATE CERTIFICATE TDECert_StandAlone
FROM FILE = ‘C:\TDE_Cert\TDECert_StandAlone.cer’
WITH PRIVATE KEY (
FILE = ‘C:\TDE_Cert\TDECert_StandAlone_PrivateKey.pvk’,
DECRYPTION BY PASSWORD = ‘MyStrongPassword@123’
);
GO
Step 6: After that we need to restore the Encrypted Database Backup on Destination Server
RESTORE DATABASE SQLMonitorUAT
FROM DISK = ‘K:\MSSQL\Backups\SQLMonitor_Full_14052025_1015AM.bak‘
WITH MOVE ‘YourEncryptedDatabase_Data’ TO ‘F:\MSSQL\DataFile\SQLMonitor_data.mdf‘,
MOVE ‘YourEncryptedDatabase_Log’ TO ‘L:\MSSQL\LogFile\SQLMonitor_Log.ldf’,
REPLACE, STATS=5;
GO
Step 7: Verify the Encryption State
Once restored the database, check whether the database is still protected by TDE or not:
USE SQLMonitorUAT;
GO
SELECT @ServerName AS [Server Name], DB_NAME(database_id) AS [Database Name],
encryption_state AS [Current Encryption State],
key_algorithm AS [Algorithm Name],
key_length AS [Key Length]
FROM sys.dm_database_encryption_keys;
GO
Note:- Even, we can re-encrypt the database with a new local certificate on Destination Server (for security compliance).
🌟 Steps to remove TDE in SQL
Steps are given below to remove the Transparent Data Encryption (TDE in SQL) from a database:
Step 1: Validate which database & certificate is used by TDE by executing below query
USE master;
GO
SELECT DB_Name(dek.database_id) AS [UserDatabaseName],
dek.encryption_state AS [CurrentEncryptionState],
cert.name AS [CertificateName],
cert.thumbprint AS [CertThumbprint]
FROM sys.dm_database_encryption_keys AS dek
JOIN sys.certificates AS cert
ON dek.encryptor_thumbprint = cert.thumbprint;
GOStep 2: After that turn Off Encryption on the Database
USE SQLMonitor;
GO
ALTER DATABASE SQLMonitor SET ENCRYPTION OFF;
GOStep 3: Now, Wait for sometime to complete the decryption process
USE master;
GO
SELECT DB_NAME(database_id) AS [Database Name],
encryption_state AS [Current Encryption State],
percent_complete AS [Percent Completed]
FROM sys.dm_database_encryption_keys;
GO| Encryption State | Description |
| 1 | Unencrypted & safe to proceed. |
| 2 | Wait until it finishes. |
| 4 | Wait until it finishes. |
Step 4: After that we can drop the Database Encryption Key (DEK)
USE SQLMonitor;
GO
DROP DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEY;
GOStep 5: Now, we can drop the certificate
USE master;
GO
DROP CERTIFICATE TDECert_StandAlone;
GOStep 6: Finally, we can drop the Master Key
USE master;
GO
DROP MASTER KEY;
GO🧽 How it works
When we enable TDE in SQL on a database, it performs below steps in the background:
- SQL Server encrypts the database encryption key (DEK) using a server certificate.
- After that, the DEK is used to encrypt all pages written to the disk.
- As data pages are read from the disk, they are automatically decrypted in memory.
This process applies equally to all database files, regardless of extension (.MDF, .NDF, .LDF).
| File Type | Description | Encrypted by TDE? |
.MDF File | Primary data file | ✅ Yes |
.NDF File | Secondary data files | ✅ Yes |
.LDF File | Transaction log files | ✅ Yes |
.BAK File | Backup files of the TDE-enabled database | ✅ Yes |
.TRN File | Transaction log backup Files | ✅ Yes |
🚩 Top 5 usage of TDE in SQL Server
Top 5 uses of Transparent Data Encryption (TDE in SQL Server) are given below for better understanding and clarity:
🔹 It Protects Data
- Purpose: It helps to encrypt the entire database, starting from data files (.mdf), log files (.ldf), to database backups.
- Benefit: It prevents unauthorized access of data if someone tries to steal or copy the database files or database backup media.
- Example: Suppose the database backup file is stolen by attackers, their system will not allow them to read the data without the encryption key.
🔹 Regulatory Compliance
- Purpose: TDE helps organizations to meet data protection laws and industry International standards for data protection like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS.
- Benefit: TDE ensures the security of sensitive data by encrypting them transparently without modifying application code.
🔹 Minimal Application Impact
- Purpose: As we aware, it works at the I/O level — It encrypts/decrypts data automatically at the time of read/write operations.
- Benefit: Hence, No need to change our existing application code, logic or queries. Encryption works in the background with minimal performance overhead.
🔹 Secure Backup & Restore process
- Purpose: It ensures that the db backup files remain encrypted, even when restored to a different server.
- Benefit: TDE protects against unauthorized database backup file restores on any other environment like test or development without the proper certificate and encryption keys.
🔹 Defense Against Insider Threats and Data Theft
- Purpose: It protects our data from internal misuse by encrypting data files on disk.
- Benefit: Even if an employee gains access to the server file system or copies database files, they cannot open or use them without encryption keys.
🏁 Conclusion
TDE, or Transparent Data Encryption in SQL Server, is a powerful data encryption feature. It helps to protect database-related files, backup files, etc. by encrypting them without any changes at the application side. But it does not secure data over network communication, it is critical for meeting compliance requirements and preventing unauthorised data exposure. By following best practices, synchronising certificates across environments, and planning for key management, organisations can successfully leverage TDE to enhance database security.
🎯 FAQs: Top 25 Interview Questions on TDE in SQL
Qns: What is TDE in SQL Server?
Ans: An encryption feature to secure data at rest.
Qns: When was TDE introduced?
Ans: SQL Server 2008.
Qns: Does TDE encrypt backups?
Ans: Yes, automatically.
Qns: Is the TDE application-transparent?
Ans: Yes, no code changes needed.
Qns: Which editions support TDE?
Ans: Enterprise (2008+), Standard (2019+).
Qns: Does TDE encrypt data in transit?
Ans: No, only data at rest.
Qns: What is DEK?
Ans: Database Encryption Key.
Qns: Where is DEK stored?
Ans: In the database boot record.
Qns: What algorithm does TDE use?
Ans: AES or 3DES.
Qns: Can you compress encrypted backups?
Ans: No, compression is ineffective.
Qns: What is the performance overhead?
Ans: Around 3–5%.
Qns: Can you use TDE with Always On AG?
Ans: Yes, with synchronised certificates.
Qns: What happens if you lose the certificate?
Ans: The database cannot be restored.
Qns: Does TDE protect tempdb?
Ans: Yes, once any database is encrypted.
Qns: What permissions are required?
Ans: CONTROL SERVER and ALTER DATABASE.
Qns: Can TDE be disabled?
Ans: Yes, by turning off encryption and waiting for decryption, you can proceed.
Qns: Is TDE FIPS compliant?
Ans: Yes, with AES_256.
Qns: Does TDE work with the Stretch Database?
Ans: No, not supported.
Qns: How to check encryption status?
Ans: Query sys.dm_database_encryption_keys.
Qns: Can you migrate a TDE database?
Ans: Yes, with the certificate.
Qns: Is TDE available in Azure SQL?
Ans: Yes, enabled by default.
Qns: What is a certificate backup command?
Ans: BACKUP CERTIFICATE … WITH PRIVATE KEY.
Qns: Can multiple databases share the same certificate?
Ans: Yes.
Qns: What is double encryption?
Ans: Using TDE with backup encryption.
Qns: What is the most common issue with TDE?
Ans: Missing certificate during restore.
Qns: Does TDE encrypt data in transit?
Ans: No, only data at rest is encrypted.
Qns: Which SQL Server editions support TDE?
Ans: Enterprise (2008+), Standard (2019+), Developer, and Azure SQL.
Qns: What is a Database Encryption Key (DEK)?
Ans: A symmetric key is used to encrypt the database.
Qns: What encryption algorithms are supported?
Ans: AES_128, AES_192, AES_256, and Triple DES.
Qns: Can TDE be enabled per table or column?
Ans: No, it encrypts the entire database.
Qns: How does TDE affect backups?
Ans: Backups are encrypted automatically.
Qns: What happens if the TDE certificate is lost?
Ans: Encrypted database and backups cannot be restored.
Qns: How to back up a TDE certificate?
Ans: Use BACKUP CERTIFICATE and include the private key.
Qns: Does TDE protect against SQL injection?
Ans: No, it only protects files and backups.
Qns: Can TDE be used with Always On AGs?
Ans: Yes, but certificates must be shared across all replicas.
Qns: What is the impact on performance?
Ans: Typically, 3–10% overhead.
Qns: How to disable TDE?
Ans: Run ALTER DATABASE SET ENCRYPTION OFF and drop the DEK.
Qns: Does tempdb get encrypted with TDE?
Ans: Yes, enabling TDE encrypts tempdb automatically.
Qns: Is TDE available in SQL Server Express?
Ans: No.
Qns: How to check the TDE status of a database?
Ans: Query sys.dm_database_encryption_keys.
Qns: Can TDE be used with Always Encrypted?
Ans: Yes, they serve different purposes.
Qns: Is TDE transparent to applications?
Ans: Yes, no code changes required.
Qns: Does TDE support backup compression?
Ans: Yes, but encryption happens after compression.
Qns: What is the role of Service Master Key in TDE?
Ans: The system protects the database master key, which protects the certificate.
Qns: Can log shipping work with TDE?
Ans: Yes, but certificates must be copied to secondary.
Qns: Can you restore a TDE-encrypted database on another server?
Ans: Yes, but only if the certificate is also restored.
Qns: What DMV shows TDE progress?
Ans: Sys.dm_database_encryption_keys.
Review the articles below, also.
LIKE Operator in SQL: Top 5 Best Usage
SQL IN Operator: Top 5 Benefits
Explore Always Encrypted: Top 5 Usage
Explore SQL Server 2025: 5 Best Usage
Explore Top 10 Features of SSMS 21
PostgreSQL vs MySQL: Top 9 Differences
Explore Sequences and Series: Top 5 Usage
SQL Window Functions: Top 5 Best Usage
Explore SQL Commands: Top 25 Commands
Understand Deadlocks in SQL Server
Explore DQS in SQL ServerExplore DQS in SQL Server
Dbcc Freeproccache: A powerful command
Extended Events in SQL Server: A Deep Dive
Understand Deadlocks in SQL Server

