PolyBase – Bridging the Gap Between Relational and Non-Relational Data
We can use Transact-SQL queries to fetch data from external data sources, such as Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) or Azure Blob Storage. It may be processed by SQL Server with the help of PolyBase, which serves as a connector, allowing these external data sources to be smoothly integrated into relational databases.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Integrating different data sources has become critical in the dynamic field of database administration. The revolutionary Poly Base technology in SQL Server transforms data access, analysis, and management by bridging the gap between relational and non-relational data. This article explores the evolution, benefits, and implementation details of Poly Base in great detail.
A Glimpse into History
Microsoft’s “Polybase” research project is where Poly Base got its start. Poly Base was first introduced in the Parallel Data Warehouse (PDW) of SQL Server 2012 with the goal of streamlining data processing for both structured and unstructured data sources.
Best Practices to Configure SQL Server on New Server
Advantages & Disadvantages of Polybase
Advantages of PolyBase
Integrated Question Answering
Standard SQL queries may be used to query both relational and non-relational data sources in PolyBase. Users may more easily deal with a variety of data sources because of this uniform approach, which also makes data processing and analysis simpler.
Performance
By utilizing SQL Server’s parallel processing capabilities, Poly Base makes it possible for it to effectively handle massive amounts of data from outside sources. The performance of queries can be greatly improved by distributing them over several nodes, particularly for intricate analytical queries.
Scalability
PolyBase is scalable, allowing it to manage large datasets. It can ensure that the system can manage enormous amounts of data without seeing a noticeable loss in performance by distributing the workload over numerous nodes in a Hadoop cluster or other compatible data sources.
Cost-Effective
By leveraging your current SQL Server infrastructure and expertise, Poly Base helps you deal with external data sources while lowering the requirement for specialized tools or resources. Cost reductions may result from this, particularly for businesses that have already invested in SQL Server technology.
Simplified Integration of Data
SQL Server external data integration is made easier with Poly Base. It enables users to access and analyze external data straight from SQL Server, doing away with the need for intricate ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) operations.
To learn more about the IO_Completion Wait Type, click here : IO_Completion Wait Type.
Disadvantages of PolyBase
Setup Complexity
Setting up the necessary external data sources and configuring Poly Base can be challenging, particularly for those who are unfamiliar with the technology. A careful design of the data distribution and other factors is required to ensure optimal performance.
Limited Support for Data Sources
Poly Base may not be able to accommodate all of the data sources that an organization uses, even if it can connect with a variety of external data sources, such as Hadoop, Azure Blob Storage, and Azure Data Lake Storage. If your data sources are diverse and non-traditional, Poly Base might not be the ideal option for integration.
Security issues
Security measures need to be properly taken into account when integrating external data sources with Poly Base. Ensuring data security and regulatory compliance may be challenging, especially when working with sensitive external data.
Overhead for Maintenance
For Poly Base to operate at its best, it has to be regularly monitored and maintained. Administrative overhead can be increased by maintaining statistics and managing dispersed data across several nodes.
Data Transfer Overhead
Even though Poly Base eliminates the requirement for ETL procedures, querying external data sources still requires data transportation overhead. Performance may be impacted by this, particularly when handling big datasets across network connections.

To learn more about the IO_Completion Wait Type, click here : CXCONSUMER Wait Type
Why do we need Poly Base in SQL Server
Relational and non-relational data from several sources may be seamlessly integrated and queried with SQL Server thanks to Poly Base. In SQL Server, Poly Base is crucial for several reasons:
Data Variety
Data may be found in many different types in contemporary corporate settings, including unstructured, semi-structured, and structured data. SQL Server can manage this diversity well because of Poly Base. Without requiring complicated ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) procedures, it may query data stored in relational database management systems, Hadoop, Azure Blob Storage, and other sources.
Unified Query Processing
With Poly Base, users may create T-SQL queries that easily retrieve and combine data from several sources. Businesses may more easily extract insights from a variety of datasets thanks to its unified query processing capabilities, which also streamlines data analysis and reporting activities.
Cost-Effectiveness
Businesses can analyze and analyze large amounts of data by utilizing their current SQL Server infrastructure thanks to Poly Base. Organizations may utilize Poly Base to integrate and analyze data without incurring considerable additional expenditures, as opposed to purchasing various tools and systems to handle different types of data.
Improved Performance
By pushing down query execution to the data source wherever possible, Poly Base maximizes query performance. For instance, Poly Base pushes query execution to Hadoop nodes if the data is stored in a Hadoop cluster. This reduces the volume of data transported over the network and enhances overall performance.
Simplified Data Management
Poly Base makes data administration duties easier by offering a unified interface for managing and querying data on several platforms. It spares database managers the time and resources they require by doing away with the necessity for intricate data migration and replication procedures.
Analysing Data in Real Time
Poly Base lets SQL Server natively access external data sources, enabling real-time data processing. For enterprises who need to get the most recent insights from continuously changing data, this capacity is essential.
Scalability
Poly Base is made to manage processing massive amounts of data. When working with large datasets, in particular, it may provide scalability and excellent performance by distributing query processing across several nodes in a Hadoop cluster.
Pre-requisites to Install PolyBase in SQL Server
Of course! Make sure your environment satisfies a few requirements before installing Poly Base in SQL Server. Transact-SQL queries on external data stored in Azure Blob Storage or Hadoop may be executed using Poly Base. The following are needed before PolyBase can be installed in SQL Server:
SQL Server Edition
SQL Server 2016 and subsequent editions support PolyBase. Verify that the edition you are using supports Poly Base features.
Operating System
Windows is the operating system on which PolyBase is supported. Make sure that the version of Windows Server that is operating on your server is compatible.
Hadoop Distribution or Azure Blob Storage
You must have a Hadoop cluster running Hadoop version 2. x or later to utilize PolyBase with Hadoop. Alternatively, you need to have access to an Azure Storage account to connect to Azure Blob Storage.
Runtime Environment for Java (JRE):
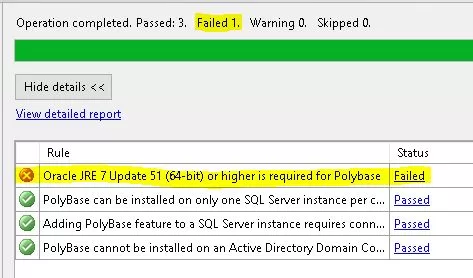
Installing the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) on the SQL Server installation is a prerequisite for using Poly Base. Install the version of JRE that works with the SQL Server version you have installed.
Configuring Azure Blob Storage or Hadoop
Configuring your Azure Blob Storage account or Hadoop cluster necessitates configuring the necessary security credentials and connection specifications. To use Azure Blob Storage, you must provide your Azure Storage account credentials or set up core-site.xml, hdfs-site.xml, and yarn-site.xml for Hadoop.
Setting Up a Network
Make sure that the Hadoop cluster, Azure Blob Storage, and your SQL Server instance have the proper network connectivity. Firewalls and network security groups need to be configured to allow communication.
PolyBase Ports
For outgoing connections, Poly Base by default uses port 17001. Verify that the SQL Server machine’s port is open and reachable.
SQL Server Configuration
You may need to adjust certain Poly Base-related settings in SQL Server Configuration Manager during the installation process. Make sure that PolyBase is properly set up and activated.
Hardware Requirements
Verify that your server satisfies the specifications for the external data sources you intend to connect to as well as the SQL Server.
Permissions
The account that runs SQL Server services and installs Poly Base has to have the right permissions on the external data sources. For instance, the account may require read/write rights on Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) folders to connect to Hadoop.
Steps to Install PolyBase in SQL Server
The instructions to install PolyBase in SQL Server are as follows:
Verify Prerequisites
Make sure your machine satisfies all the requirements listed in the preceding response before installing PolyBase.
Launch the Wizard to Install SQL Server
Open the wizard for installing SQL Server.
Choose “New SQL Server stand-alone installation or add feature to an existing installation.”
Select Features
Choose “PolyBase Query Service for External Data” from the “Database Engine Services” node in the Feature Selection box. Installing PolyBase is made possible by this option.

During installation, specify the location of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE). JRE is used by SQL Server to connect to Poly Base.
Setting up PolyBase Ports
The default port for external connections of PolyBase is 17001. This port can be changed if needed. Make sure the port you have chosen is available and open.
To configure connectivity for PolyBase
Set up Poly Base to connect to Azure Blob Storage or your Hadoop cluster during installation. For Hadoop, provide the location of the core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml files, and for Azure Blob Storage, provide the Azure Storage account credentials.
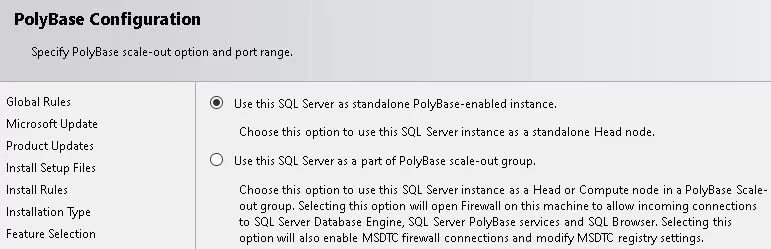
Finish Up with the Installation
Carry out the installation procedure. Poly Base and other features that you have chosen will be installed via the wizard.
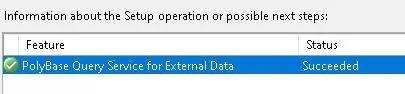
Check the Installation of PolyBase
Verify Poly Base installation by looking for Poly Base-related objects and services in the SQL Server instance once the installation is finished.
Poly Base searches against external data sources may be effectively executed using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
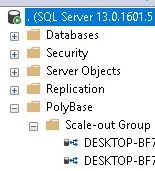
Examine PolyBase Queries
To confirm connection and data extraction from external sources, test Poly Base queries. Make sure the queries provide the desired outcomes.
Set Up External Data Sources for PolyBase
After installation, create external tables pointing to Azure Blob Storage or your Hadoop cluster to establish Poly Base external data sources. Describe the external data’s location and structure in these tables.
Observe and uphold:
Configure monitoring to keep tabs on Poly Base performance and address any problems with query execution or connectivity.
To guarantee peak performance, keep an eye on the system resources and logs connected to Poly Base.
Security Points to Remember:
Put security mechanisms in place to safeguard data access and Poly Base connections, such as authorization and authentication.
SQL Server Version Wise PolyBase Enhancements
SQL Server’s Poly Base functionality facilitates the integration and querying of non-relational and relational data from several sources. Since its launch, Poly Base has had several improvements in various SQL Server versions, enhancing both its functionality and speed. An outline of Poly Base improvements over SQL Server versions is shown below:
SQL Server 2016
Introduction of PolyBase
The SQL Server 2016 Parallel Data Warehouse version marked the debut of Poly Base. It made it possible for SQL Server to use T-SQL commands to query Hadoop data.
SQL Server 2017
Expanded Data Sources
SQL Server 2017 extended Poly Base’s functionality beyond Hadoop by introducing support for other data sources, such as Azure Data Lake Store and Azure Blob Storage.
Improved Performance
Poly Base query speed has been enhanced, making it more effective when handling massive amounts of data from outside sources.
SQL Server 2019
Big Data Clusters
Big data clusters were introduced in SQL Server 2019 and combined Spark, Hadoop, and SQL Server into a single data platform. These clusters relied heavily on Poly Base, which allowed for easy querying and data integration between relational and big data sources.
Virtualization of Data
Data virtualization was made possible by Poly Base in SQL Server 2019 and allowed users to query and analyze external data without having to copy or relocate it into a SQL Server database. This functionality made data management duties more simpler.
Enhanced Security
To provide safe access and data transfer between SQL Server and external data sources, SQL Server 2019 improved Poly Base security capabilities.
Support for Oracle
SQL Server 2019’s Poly Base now supports Oracle database queries, extending its reach to more relational databases.
Better Pushdown of Query
With the release of SQL Server 2019, query pushdown capabilities were enhanced, allowing for more effective processing by transferring less data and improving overall performance by shifting portions of the query execution to the data source.
SQL Server 2022
Quicker Loading of Data
Faster data loading from external sources into SQL Server tables is now possible thanks to improvements made to Poly Base data loading speed in SQL Server 2022.
Improved Performance of Queries
Ongoing enhancements to query performance, maximizing the execution of Poly Base queries for extensive data processing and analysis.
Additional Data Format Support
Data saved in diverse file formats may now be more easily integrated and queried thanks to SQL Server 2022’s expansion of Poly Base’s support for multiple data formats.
Differences Between PolyBase and Linked Server
The following table lists the distinctions between SQL Server’s PolyBase and Linked Server:
| Aspect | PolyBase | Linked Server |
| Definition | With PolyBase, you may use T-SQL to query external data stored in Azure Blob Storage or Hadoop. | With SQL Server, you may connect to an external data source and run queries against it using the Linked Server capability. |
| Data Sources | Supports external data sources such as Azure Blob Storage and Hadoop. | Supports a large number of data sources, such as Excel, Oracle, MySQL, and more SQL Server instances. |
| Performance | Due to its ability to handle data in parallel, this method often offers greater performance for large-scale data processing jobs. | The kind of connected server and query complexity can have an impact on performance. |
| Data Movement | Stores metadata about external data in external tables. There is no transfer of data into SQL Server; it remains in external sources. | Data can be sent between servers, enabling the consolidation or transformation of data before it is used. |
| Query Language | Query Language T-SQL is used to directly query external data sources. | Requires familiarity with the external data source’s unique query language. |
| Integration | Integration Easily query external data using common T-SQL queries thanks to integration with SQL Server. | Requires connected server objects to be explicitly created and configured. |
| Security | Supports safe connections to Hadoop clusters using Kerberos authentication. | Needs security settings for authorization and authentication to be configured according to the external data source. |
| Ease of Use | Simpler to set up and utilize when retrieving data from Azure Blob Storage or Hadoop. | More complicated and necessitates extra setup processes, particularly when working with several data source types. |
| Scalability | Because of its parallel processing capabilities, it scales effectively for large-scale data processing jobs. | The external data source’s and the associated server’s limits and performance might have an impact on scalability. |
| Supported Versions | Accessible in versions of SQL Server 2016 and later. | Accessible in different SQL Server versions. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How does PolyBase differ from conventional database connections and what does it mean?
Ans: A feature of SQL Server data virtualization called PolyBase enables users to access and analyze data from other sources right from SQL Server, including Hadoop and Azure Blob Storage. PolyBase streamlines data processing and analysis by integrating non-relational data into the relational database system without the need for standard connections.
Q2: Is PolyBase capable of effectively managing massive amounts of data?
Ans: PolyBase is built to effectively manage massive amounts of data. PolyBase guarantees excellent performance even with large datasets by using distributed computing capabilities and concurrent query processing.
Q3: What are the main drawbacks of PolyBase?
Ans: PolyBase has several drawbacks, such as its support for a small number of data types, possible configuration complexity, and reliance on the availability of external data sources. Comprehending these constraints is imperative for efficient execution and employment.
Q4: How can I resolve connection problems with PolyBase?
Ans: Checking firewall settings, confirming network setups, and making sure SQL Server and external data sources are compatible are all necessary steps in troubleshooting PolyBase connectivity difficulties. In-depth error messages seen in SQL Server logs offer important information for identifying and fixing connection issues.
Q5: Is PolyBase compatible with cloud-based data storage solutions?
Ans: Yes, PolyBase works with several cloud-based data storage options, such as Azure Data Lake Storage and Azure Blob Storage. Because of its adaptability, customers may easily incorporate data from cloud platforms into their SQL Server setup.
Conclusion
PolyBase is evidence of Microsoft’s dedication to reducing the complexity of data integration. Businesses can fully use the potential of their heterogeneous datasets thanks to their ability to bridge the gap between relational and non-relational data sources. Organizations may ensure a smooth data integration experience by making educated decisions by knowing the background, benefits, drawbacks, and implementation nuances of PolyBase.
Review the below articles also
SQL Managed Instance: Faster & Improved
TSQL Database Backup: Top 7 Usage
Decommission A Server: In 6 Easy Steps
Discover Recovery Model in SQL Server